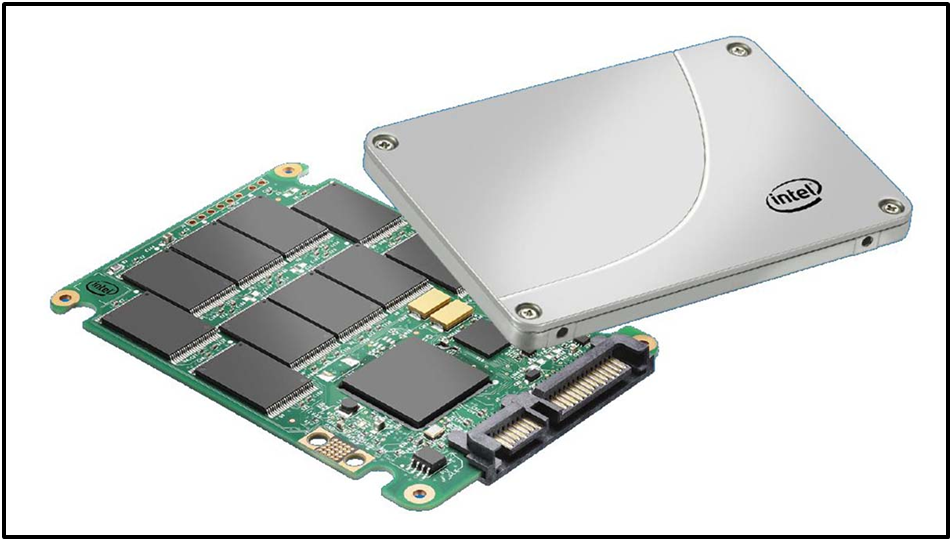
Upgrading to a solid state drive is one of the easiest and most effective ways to speed up a computer. SATA SSDs, in particular, offer a reliable balance of performance, compatibility, and price, making them ideal for desktops, laptops, and even some servers.
But not all SATA SSDs are created equal. From endurance ratings to controller types, choosing the right one depends on how and where it will be used.
What Makes SATA SSDs a Solid Choice?
SATA SSDs connect via the Serial ATA interface, the same port used by traditional hard drives. This makes them highly compatible with a wide range of systems, including older desktops and laptops.
Although not as fast as NVMe solid state drives, SATA SSDs still offer a massive performance boost over spinning hard drives. Faster boot times, quicker file transfers, and snappier system responses are just a few of the benefits.
They’re also more affordable than NVMe drives, making them a smart pick for users who want a good blend of speed and value without overpaying for top-tier specs they may not need.
Key Factors to Consider When Buying a SATA SSD
1. Capacity Needs
Think about how much storage you really need. A 240GB or 500GB SSD is usually enough for everyday users who mainly need faster system performance and storage for basic apps. However, power users or creative professionals may want 1TB or more to handle larger files and workloads.
2. Read/Write Speeds
Most SATA SSDs max out at around 550MB/s read and 500MB/s write speeds. While this is significantly faster than traditional hard drives, it’s important to compare drives because some cheaper models may not sustain these speeds under heavy workloads.
3. Endurance (TBW and MTBF)
Endurance ratings are often shown as TBW (Terabytes Written) or MTBF (Mean Time Between Failures). A higher TBW means the drive can handle more data written over time—important for content creators, video editors, or users running virtual machines.
4. DRAM vs DRAM-less
Some budget SATA SSDs are DRAM-less, meaning they use system RAM or a small cache to manage data instead of dedicated onboard memory. These are fine for light tasks but might slow down during large file transfers or multitasking.
5. Warranty and Support
Many reputable SSD brands offer 3 to 5 years of warranty. Always check the terms, as longer warranties often signal better reliability and build quality.
Where SATA SSDs Excel
SATA SSDs work well in many situations:
- Home and Office Computers: For email, web browsing, and office apps, a basic SATA SSD makes a noticeable difference in speed and system responsiveness.
- Secondary Storage: If your primary drive is an NVMe SSD, a SATA SSD works well as a secondary drive for media, games, or backups.
- Low-Cost System Upgrades: Replacing an old hard drive with a SATA SSD is one of the most affordable ways to breathe new life into aging laptops or desktops.
- Data Centers on a Budget: Some small servers and virtual machines still benefit from the consistent performance of SATA SSDs where extreme speed isn’t required.
Comparing SATA with NVMe and M.2 Drives
NVMe and SATA are not competing technologies—but rather different performance tiers. NVMe drives, especially those in M.2 form factors, connect via the PCIe bus and offer significantly higher read/write speeds—often over 3,000MB/s.
However, for many users, these performance differences are only noticeable during heavy workloads like video rendering or massive file transfers. Unless your daily tasks demand such performance, a well-chosen SATA SSD is usually more than sufficient.
Those with newer systems might explore M.2 solid state drives, which offer compact size and high-speed performance. Just be sure to confirm compatibility, as not all M.2 slots support NVMe.
SATA SSD Installation Tips
Installing a SATA SSD is typically straightforward. Here are a few steps to keep in mind:
- Backup Your Data: Before any upgrade, make sure to back up all important files.
- Use a Mounting Bracket if Needed: Most SSDs are 2.5″ and may require an adapter for 3.5″ bays.
- Update Firmware: Check the manufacturer’s website for the latest firmware updates to ensure optimal performance and stability.
- Enable AHCI in BIOS: This setting ensures the drive runs at maximum speed.
Who Should Still Choose SATA SSDs?
While NVMe and M.2 drives are rising in popularity, SATA SSDs still make sense for many users:
- Budget-conscious buyers
- Older systems with no M.2 slot
- Secondary or backup drives
- General users who don’t require extreme speed
SATA SSDs strike the right balance between speed, cost, and compatibility, especially when sourced from trusted vendors, who offer pre-tested components and support that simplify the upgrade process.
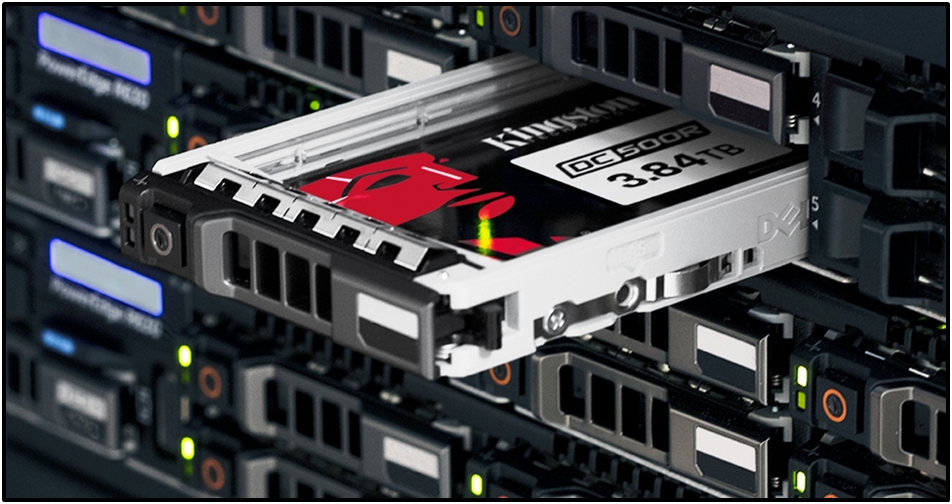

Built for Real-World Performance
Choosing the right SATA SSD depends on your workflow, system specs, and performance expectations. While faster drives exist, many users won’t notice the extra speed of NVMe unless their work specifically demands it.
A reliable SATA SSD can drastically cut load times, reduce system lag, and boost productivity, all without breaking the bank. For most day-to-day computing needs, it’s still one of the best investments you can make.
To make the process easier, explore pre-tested SATA SSDs from Cloud Ninjas, a trusted source for performance hardware, expert guidance, and seamless upgrades.
READ ALSO: BUY KVM VPS WITH NVMe STORAGE: SPEED AND VIRTUALIZATION POWER











